Pierre: Solving Problems By Intelligent Search
Realized in 2017 Tags: c, A*
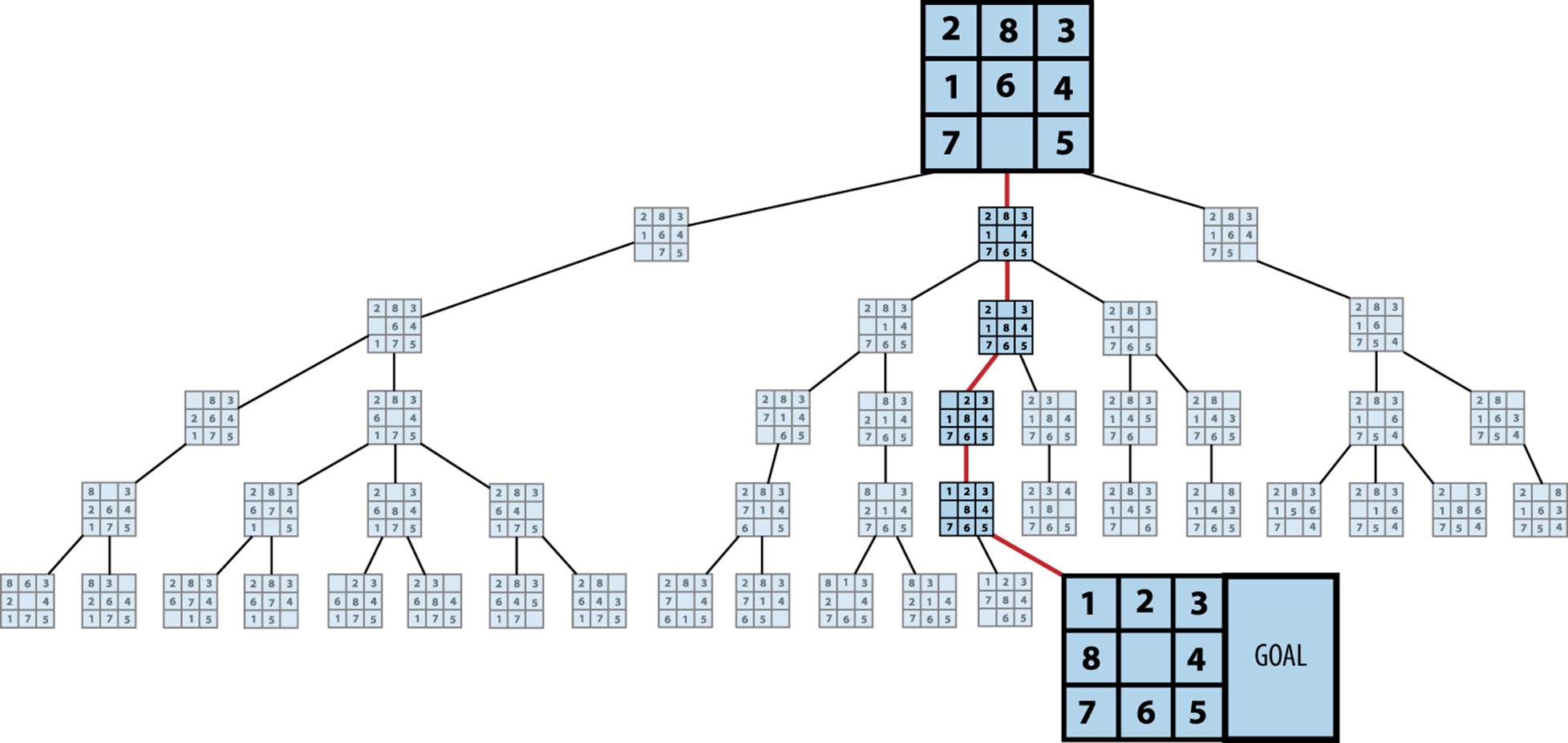
This project is completely related to the third chapter of Artificial Intelligence A Modern Approach . The idea is to solve any problems without having to re-implement the algorithms every time and to provide a different resolution strategy to solve each problem. To achieve this goal I use
Index
States and Actions
Before we start talking about strategies to solve problems, we must introduce the basic elements of the problem:- State: represent the internal situation of the problem at a given moment. In the state are represented only the information necessary for the resolution of the problem. It could be a vector, a matrix or a struct so I used a void pointer to be more generic possible;
- Action: an action is a function that generates a new state from a given state;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | typedef struct State { long int id; void* state; } State; typedef struct Action { State* (*move)(State* old_state); } Action; |
(Full code is available here).
Formulating problems
Now let's talk about the problem description that the software needs to solve it:- Initial State: defines the initial state of the problem;
- Transition model: given a state and legal action in it, it calculates a list of all possible states reachable by executing that action in that state;
- Goal test: which determines whether a given state is a goal state;
- Cost Function: function that assigns a numeric cost to each nodes, based on the distance from the initial state;
- Constraint Test Function: determines if the state on which it is applied respects the constraints of the problem;
- Heuristic Function: estimates a numeric cost of the path from the node on which it is applied up to the target state;
- Step cost: given a state and the respective cost, returns the cost of its successor node;
- State Compare: given two states defines its equality or not;
- Print Function: given a status, defines how to print the contents on the screen;
NB: some of these functions will not available in "problem" struct but there are needed to support other key functions, just like public and private methods. (For example, the Constraint Test Function used by the Transaction Model)
I represented these concepts in the source code in this way:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | typedef struct Problem { State* initial_state; long int depth_solution; List* (*transition_functions)(State* state); Boolean (*goal_test)(State* state); void (*print_state)(State* state); int (*heuristic)(State* state); int (*step_cost)(State* state, int cost); int (*state_compare)(void* state1, void* state2); } Problem; |
(Full code is avaible here).
Node Structure
Each algorithm does not work directly on the problem but works on a graph where each node contains information about the respective status of the problem. Now we see the internal structure of the node:- Node status: the status of the problem, hosted in the node;
- Parent Node: a pointer to the parent of the current node;
- Action: the action performed on the parent node that led to the creation of the current node;
- Path Cost: the cost of the path from the root node to the current node;
- Heuristic Cost: estimate of the cost of the path from the current node to the goal node;
- Total Cost: sum of the Path Cost and the Heuristic Cost;
- Child Function: function that from the current node, through an "action", generates all the possible child nodes;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | typedef struct IA_Node { long int id; struct State* node_state; struct IA_Node* parent; struct Action* node_action; float path_cost; float heuristic_Cost; float total_cost; struct IA_Node* (*child_ia_node)(struct Problem* problem, struct IA_Node* actual, struct Action* move); } IA_Node; |
(Full code is avaible here).
Internal logic
Pierre (the name came from the pronunciation of PR that stand for Problem Resolver) is just a menu with which the user interacts.
It will print to him a list of the already implemented problem to solve. When he has chosen one of them, it provides him a list of algorithms to use to solve it. (for example, I have already implemented the lake problem and the 8-puzzle problem. The first one is very easy to solve, the second one needs to a heuristic function).
These algorithms use a classic data struct like priority list or red-black tree but also a node struct described above.
The struct node needs to the struct that describes the problem.
So you need to implement the required functions to describe your problem. (we talked about it here)
To do this you need to import a common.h that, in addition to providing functions for creating and use a list, provide also the state and action struct.
//Internal scheme of Pierre
pierre.h
|
algorithms.h
/ | \
/ | \
priority_list.h node.h redblack_tree.h
|
problem.h
|
*Problem_to_solve*
|
common.h
|
list.h
Implemented Algorithms
The following paragraph is a list of all the implemented algorithms that can be found in the source code , followed by a brief description:
- Breadth-first: search expands the shallowest nodes first; it is complete, optimal for unit step costs, but has exponential space complexity.
- Uniform-cost: search expands the node with lowest path cost, g(n), and is optimal for general step costs.
- Depth-first: search expands the deepest unexpanded node first. It is neither complete nor optimal, but has linear space complexity.
- Depth-limited: search adds a depth bound.
- Iterative deepening: search calls depth-first search with increasing depth limits until a goal is found. It is complete, optimal for unit step costs, has time complexity comparable to breadth-first search, and has linear space complexity.
- A*: search expands nodes with minimal f(n) = g(n) + h(n). A∗ is complete and optimal, provided that h(n) is admissible (for TREE-SEARCH) or consistent (for GRAPH-SEARCH). The space complexity of A* is still prohibitive.
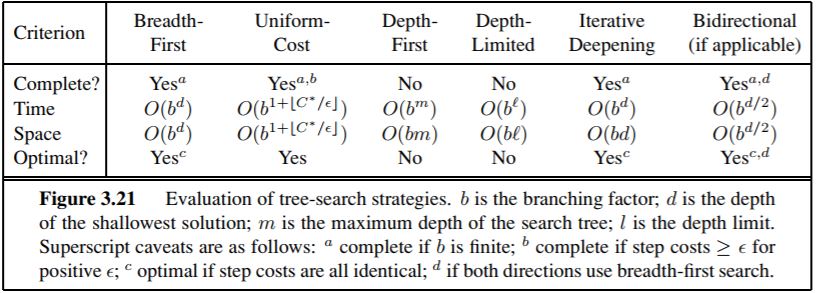
This entire paragraph is a quote from Solving Problems by Searching - Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach (3rd Edition).At the end of the article I left you an example of the running program: